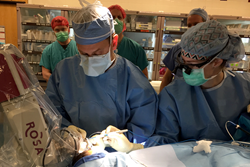
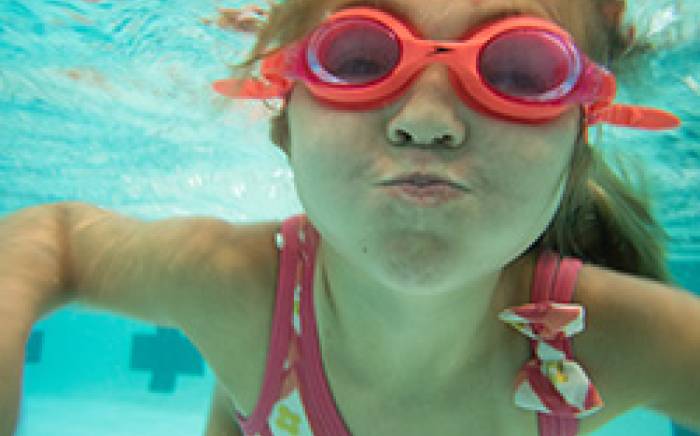Surgical robot assists with epilepsy treatment
Washington University neurosurgeons at St. Louis Children’s Hospital are now using a new generation of robotic technology to help identify the source of seizures in patients with epilepsy. The advantages of using the ROSA™ robotic surgical assistant include:
- Significantly less invasive means of obtaining information about activity recorded from within the brain
- Surgical time is reduced from more than six hours to two hours
- Recovery time is greatly reduced: return to daily activities within days of the procedure rather than weeks
- Removal of only a small amount of hair
 What is stereotactic EEG?
What is stereotactic EEG?
An electroencephalogram (EEG) is a test used to detect abnormal electrical activity in the brain. Its purpose is to track and record brain wave patterns. To conduct the test, electrodes—small, flat metal discs—are placed on the scalp, and signals are sent to a computer and recorded.
For some patients with epilepsy, it is beneficial to record brain activity directly from the surface of the brain (cortex) or deeper within the brain. This information can pinpoint the precise location of abnormal activity causing seizures.
In the past, the only way neurosurgeons could place electrodes directly on the brain’s surface was to remove a large section of a patient’s skull. Called a craniotomy, this invasive surgery—necessary for fuller access to the brain—can be uncomfortable and requires weeks of recovery time.
A stereotactic EEG (sEEG) eliminates the need for a craniotomy. During this procedure, neurosurgeons make multiple tiny, precise incisions called burr holes in the skull. Through these, electrodes may be placed in the cortex as well as deeper within the brain. This less invasive approach means patients have less discomfort, recover more quickly and have a smaller risk of infection.
What is ROSA™?
The innovative ROSA robotic device, produced by MedTech Surgical, serves as both a surgical assistant and GPS for the brain during sEEG planning and implantation.
When planning an sEEG, neurosurgeons and epileptologists (neurologists specializing in the treatment of epilepsy) use ROSA’s computer to make 3-D maps of a patient’s brain using preoperative MRI and CT scans. These images help determine where to place electrodes and what paths to use to get to those areas. That data is then entered into ROSA. During the procedure, neurosurgeons control ROSA’s robotic arm while it uses the mapping information to direct the placement of electrodes through the pre-planned pathways. Once at the target destinations, neurosurgeons can use ROSA to guide needle-thin instruments to identify the brain areas where seizures occur and, when appropriate, remove them, either with conventional neurosurgical approaches or using laser ablation.